正高级
Supervisor of Doctorate Candidates
Supervisor of Master's Candidates
Hits:
DOI number:10.1039/D0CP06207C
Affiliation of Author(s):Yangzhou University
Journal:Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics
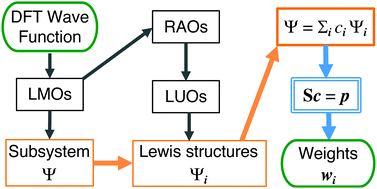
Abstract:Due to methodological difficulties and limitations of applicability, a quantitative bonding analysis based on the theory of resonance is presently not as convenient and popular as that based on the molecular orbital (MO) methods. Here, we propose an efficient quantitative resonance theory by expanding the DFT wave function in terms of a complete set of Lewis structures. By rigorously separating the resonance subsystem represented by a set of localized MOs, this approach is able to treat large molecules, nonplanar π-conjugate systems, and bonding systems mixing both σ and π electrons. Assessment in 2c-2e systems suggests a new projection-weighted symmetric orthogonalization method to evaluate the weights of resonance contributors, which overcomes the drawbacks of other weighting schemes. Applications to benzene, naphthalene and chlorobenzene show that the present method is insensitive to the basis set employed in the DFT calculations, and to the choices of the independent Lewis set determined by Rumer's rule. Advanced applications to diverse chemical problems provide unique and valuable insights into the understanding of hydrogen bonding, the π substituent effect on benzene, and the mechanism of Diels–Alder reactions.
First Author:Yang WANG
Indexed by:Article
Discipline:Natural Science
Document Type:SCI
Volume:23
Page Number:2331-2348
Translation or Not:no
Date of Publication:2020-12-18
Included Journals:SCI
Links to published journals:https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2021/cp/d0cp06207c